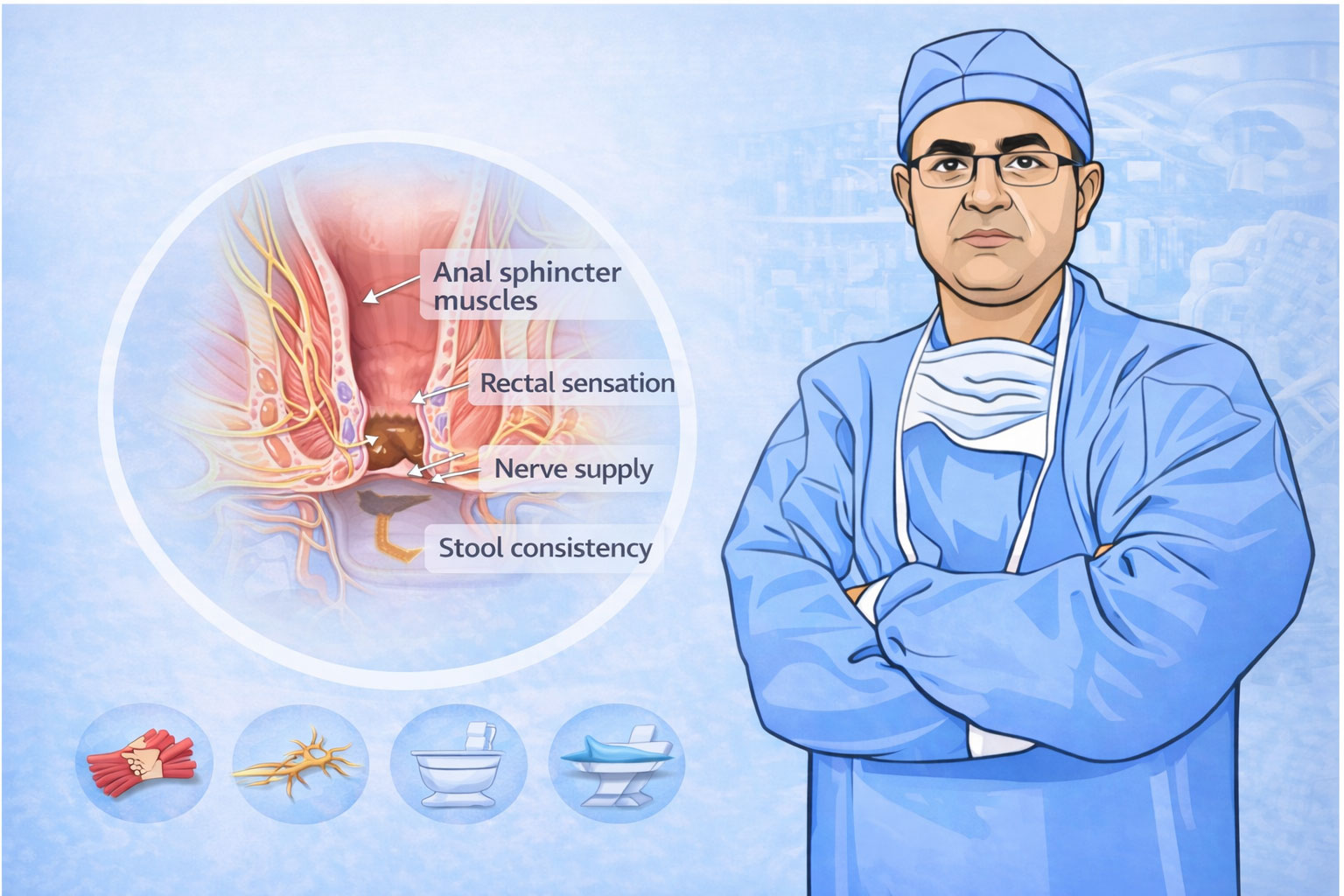
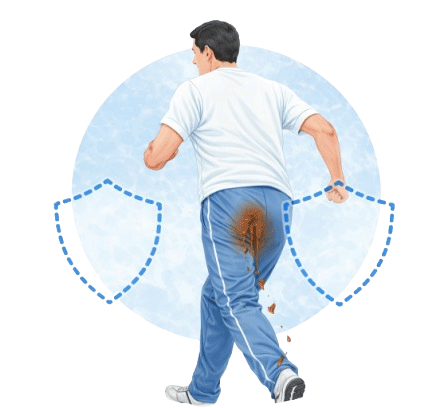
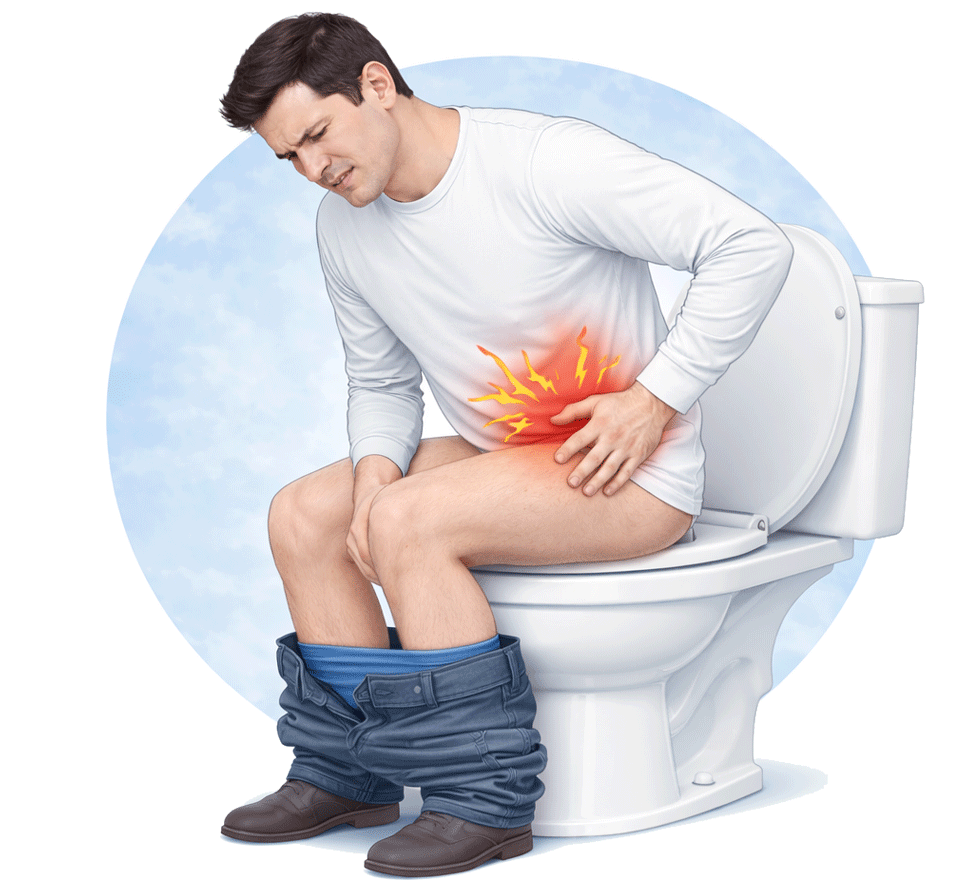
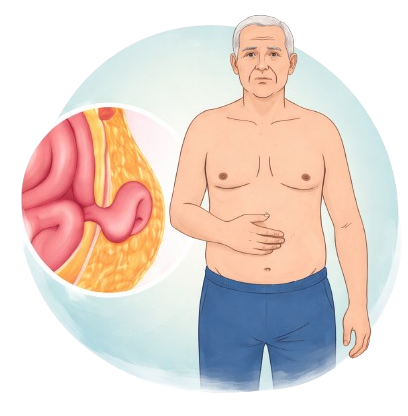

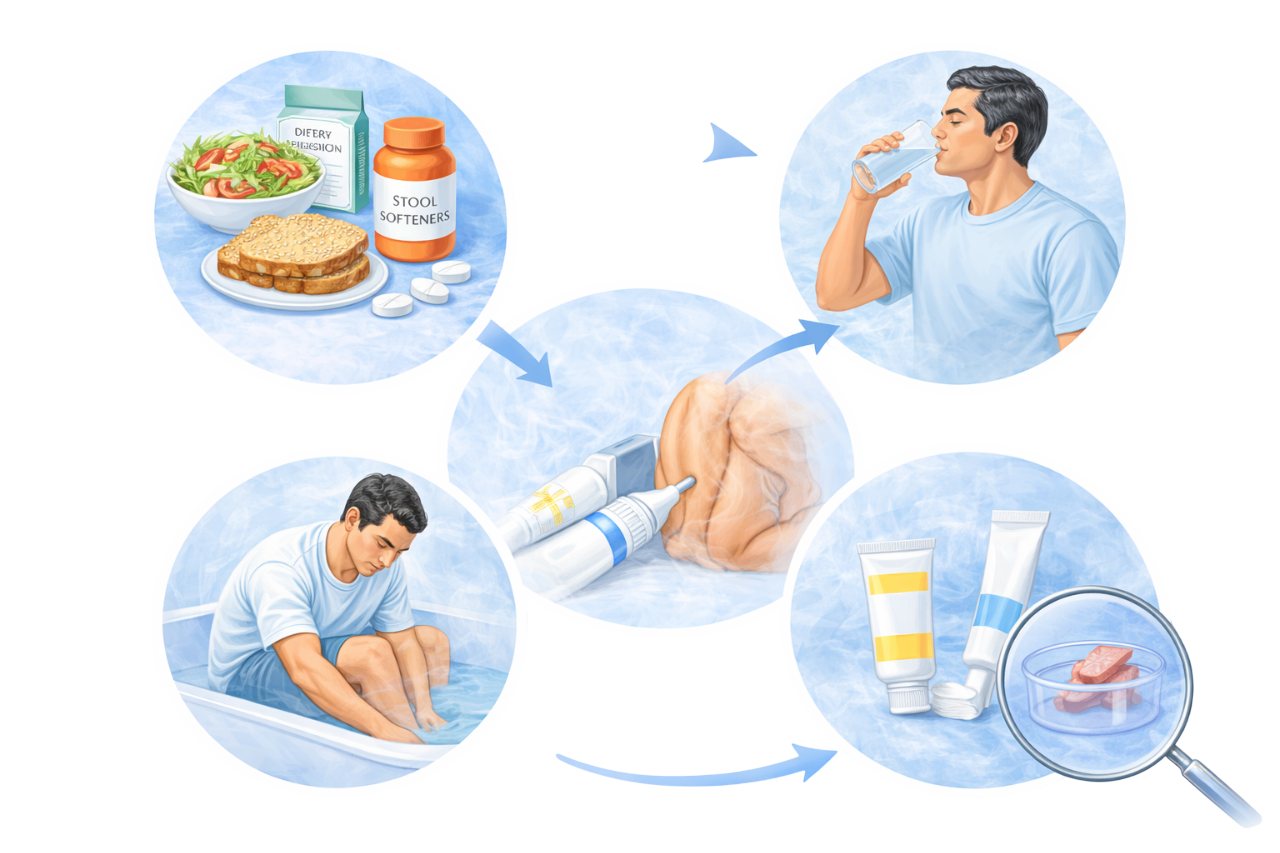
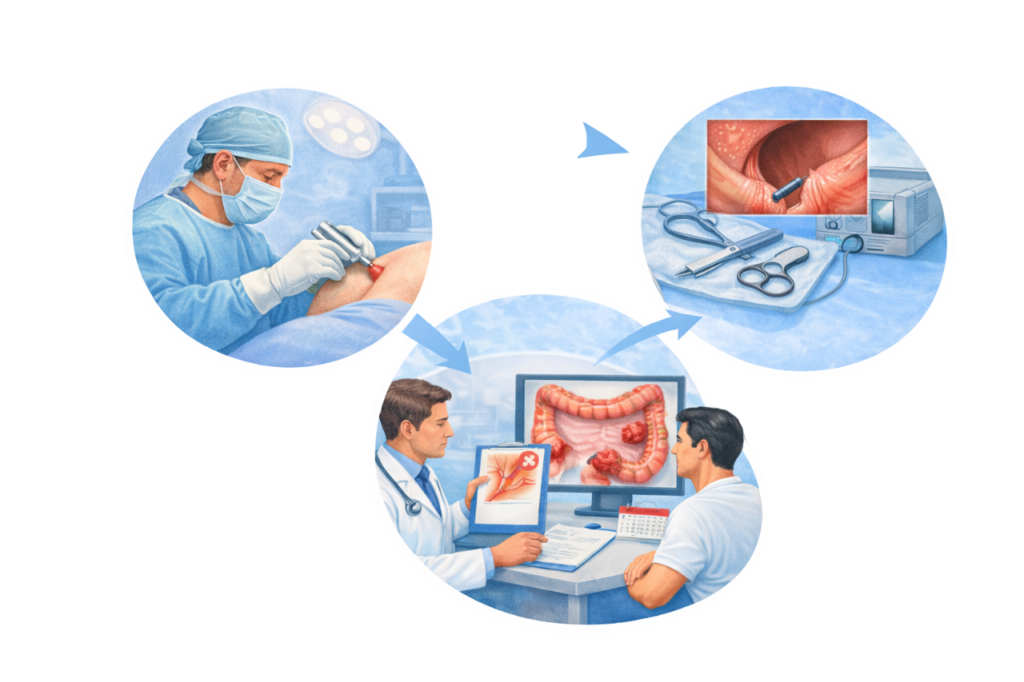
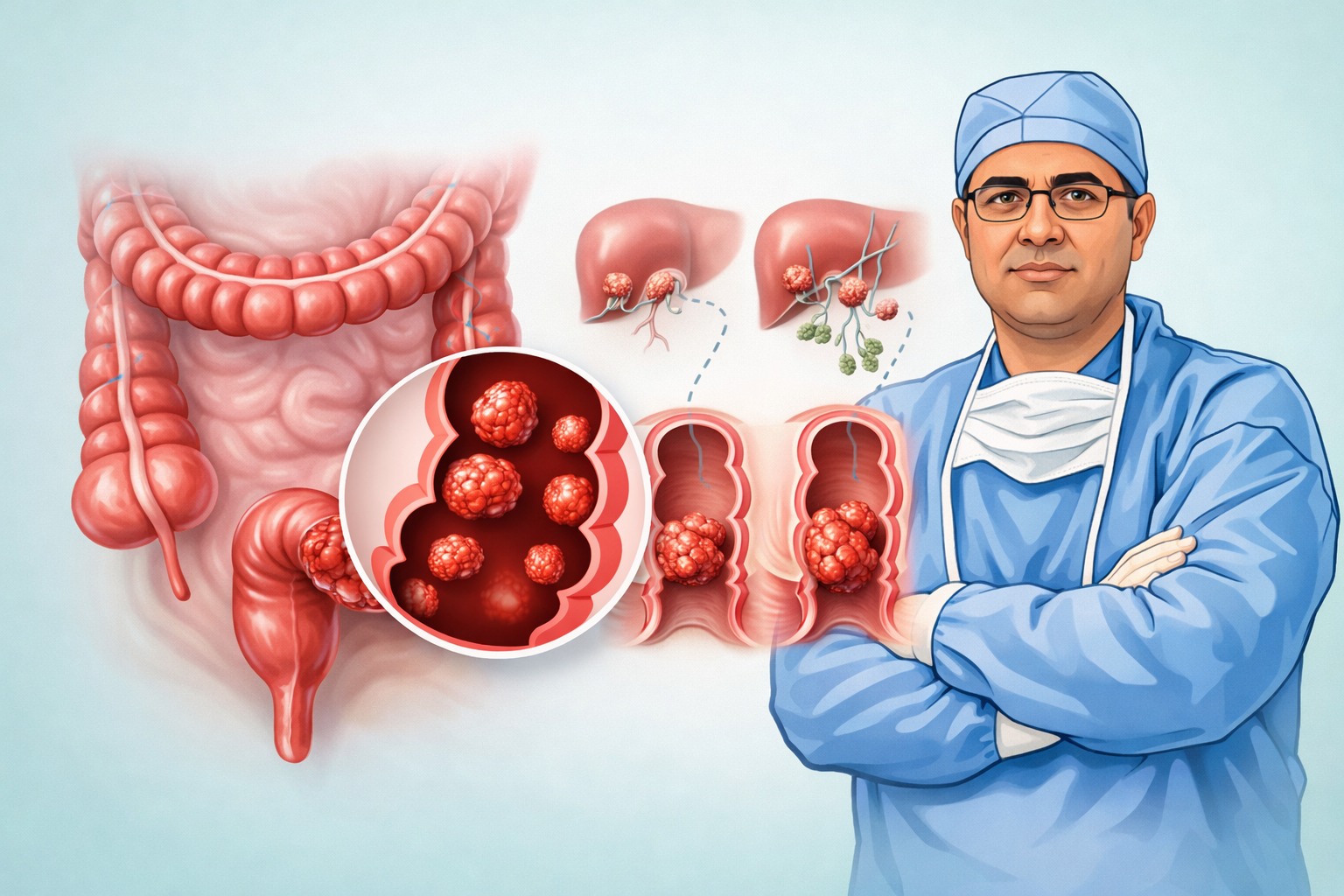
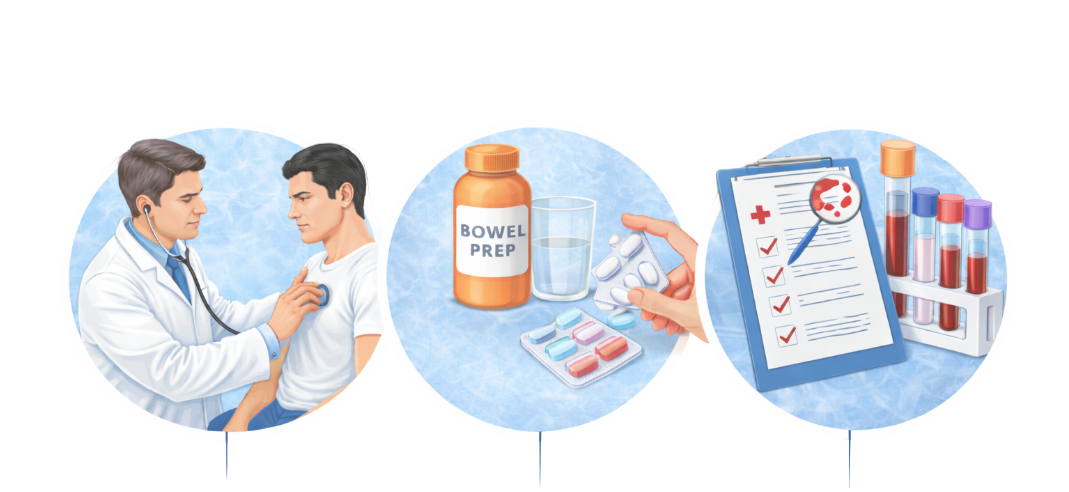
The information provided on this page is for general educational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Treatment decisions should be made after consultation with a qualified medical professional, based on individual clinical evaluation.


Dr. Rajeev Kapoor is a practicing surgeon based in Mohali, Punjab. He provides clinical services in the field of gastrointestinal, colorectal, and general surgery. This website is intended for informational and educational purposes only.
WhatsApp us