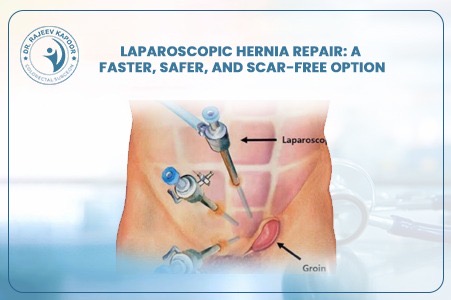
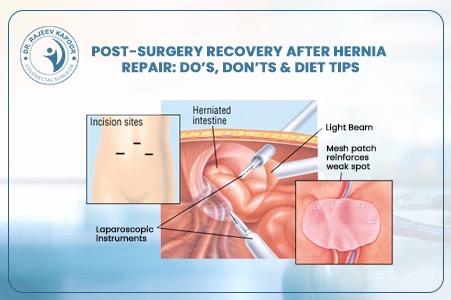
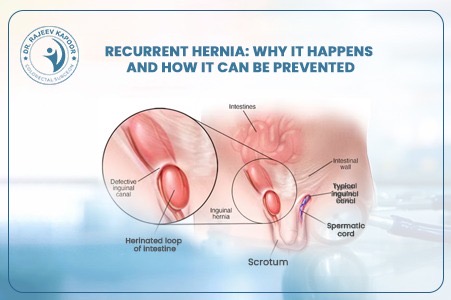
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair: A Faster, Safer, and Scar-Free Option
Gone are the days when hernia surgery meant long incisions, painful recovery, and weeks away from work. With the advent of laparoscopic hernia repair, patients now enjoy a quicker, safer, and far more comfortable experience. “Laparoscopy has transformed hernia treatment into a day-care procedure — patients walk home the same day with minimal pain,” says Dr. Rajeev Kapoor, senior gastrointestinal and laparoscopic surgeon in Chandigarh. 1️⃣ What Is Laparoscopic Hernia Repair? Laparoscopic hernia repair, also known as keyhole surgery, involves repairing the hernia through three tiny incisions (each about 0.5–1 cm). A thin tube with a camera (laparoscope) is inserted to provide a magnified, high-definition view of the internal structures. Using specialized instruments, the surgeon gently pushes the protruding tissue back into place and reinforces the weak spot with a surgical mesh, ensuring long-term strength. 2️⃣ How It Differs from Open Surgery Aspect Open Hernia Repair Laparoscopic Hernia Repair Incision Size 6–10 cm (large cut) 0.5–1 cm (keyhole) Pain & Recovery Moderate to high pain, longer rest Minimal pain, rapid recovery Hospital Stay 2–4 days Same-day discharge (24 hrs max) Scarring Visible scar Nearly invisible Recurrence Rate Slightly higher Very low when done by experts Return to Work 10–15 days 3–5 days “With modern mesh technology and precision tools, laparoscopic surgery ensures faster healing and excellent long-term results,” notes Dr. Kapoor. 3️⃣ Who Can Benefit from Laparoscopic Hernia Surgery? Laparoscopic repair is suitable for: Inguinal (groin) hernias — the most common type in men Bilateral hernias (both sides) Recurrent hernias (after open surgery) Umbilical and incisional hernias Obese patients, where open surgery carries more risk However, for very large or complicated hernias, Dr. Kapoor carefully evaluates whether a minimally invasive approach is the safest option. 4️⃣ Step-by-Step: The Laparoscopic Procedure General anesthesia is given for patient comfort. Small incisions are made near the navel. A laparoscope provides a magnified view of the hernia and surrounding tissue. The protruding tissue is gently repositioned inside the abdomen. A medical-grade mesh is placed over the weak area to reinforce the wall. The incisions are closed with absorbable sutures — leaving minimal or no visible scar. The entire procedure typically takes 45–60 minutes. 5️⃣ Recovery and Post-Surgery Care Walking: Within 4–6 hours post-surgery Diet: Light meals on the same day Return to Work: Usually within 3–5 days Exercise/Lifting: Avoid heavy weights for 4–6 weeks Follow-Up: Regular reviews ensure healing and prevent recurrence “Most of my patients resume routine activities within a week — it’s that smooth and safe,” shares Dr. Kapoor. 6️⃣ Advantages of Laparoscopic Hernia Repair ✅ Smaller incisions, minimal pain ✅ Shorter hospital stay or same-day discharge ✅ Early mobility and faster return to daily life ✅ Reduced infection and recurrence rates ✅ Cosmetic benefit – almost no visible scar 7️⃣ Why Choose Dr. Rajeev Kapoor for Hernia Surgery Over two decades of surgical expertise in gastrointestinal and laparoscopic procedures Specialized in complex hernias and recurrent cases Uses international-grade mesh and advanced laparoscopic systems Focus on patient comfort, precision, and long-term success Conclusion Laparoscopic hernia repair represents the future of hernia management — safe, effective, and minimally invasive. For patients seeking faster recovery, smaller scars, and lasting relief, it’s the clear choice. Dr. Rajeev Kapoor, one of Chandigarh’s most trusted laparoscopic surgeons, offers advanced hernia care using the latest global techniques and technologies — ensuring both comfort and confidence.